Here are some points for lower leg clot symptoms:
1. Understanding Lower Leg Clots
2. Lower Leg Clot Symptoms
3. Risk Factors for Developing Lower Leg Clots
4. When to Seek Medical Attention
5. Diagnostic Methods for Lower Leg Clots
6. Treatment Options for Lower Leg Clots
7. Preventive Measures Against Lower Leg Clots
8. Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk of Lower Leg Clots
9. FAQ’s
10. Conclusion
1. Understanding Lower Leg Clots
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is another name for lower leg clots is result of blood clot that develops in leg deep veins. If clot breaks free and moves to lungs causing pulmonary embolism this disease may result in major health problems. Knowing signs of lower leg clot is important for prompt identification and management.
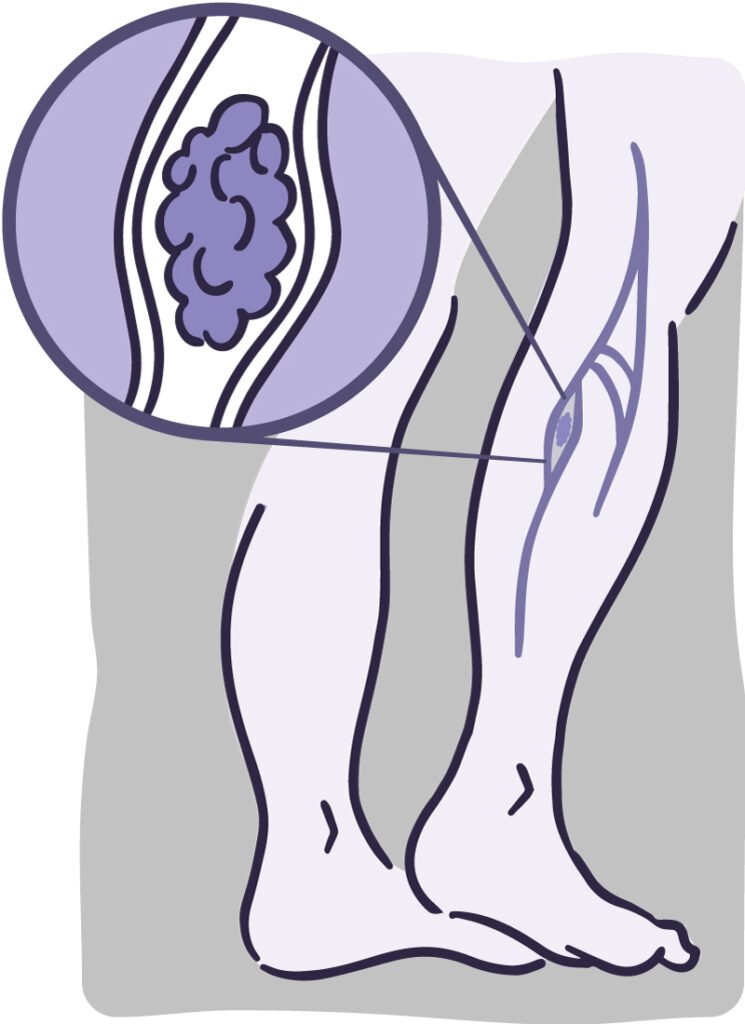
2. Lower Leg Clot Symptoms
It is important to knowing symptoms of lower leg clots to act quickly. This are the most typical signs:
- Swelling: One leg usually in calf region may appear larger than other. Swelling may be slight or significant.
- Pain or tenderness: You may feel pain or tenderness in affected leg specially calf. Discomfort may include pain or pulling sensation.
- Red or discolored skin: Skin around affected area may have reddish-blue tint.
- Warmth: Compared to other leg affected leg may feel warmer to touch.
- Big veins: Superficial veins may swell or become more noticeable.
- Homan’s sign: Homan’s sign test is performed by some medical professionals and involves bending leg slightly upwards. Although it is not guarantee calf pain during this motion may indicate DVT.
- Fatigue: One leg feels tired or heavy in affected area.
You must seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of this symptoms specially if they appear suddenly or for no apparent reason.
3. Risk Factors for Developing Lower Leg Clots
There are several conditions that increase chances of developing lower leg clot. Among them are:
- Long immobility: Long time spent sitting or lying down such as on long flights or while recovering in bed can reduce blood flow and increase risk of clots.
- Injury or surgery: Damage to vein as result of injury or surgery can cause development of clot.
- Hormonal factors: Pregnancy, hormone therapy and birth control pills can all cause hormonal changes that increase risk of clotting.
- Overweight: Being overweight puts extra strain on veins which impedes normal blood flow.
- Smoking: Smoking increases risk of blood clots by damaging blood vessels and reducing circulation.
- Age: Chance of developing DVT increases with age specially in people over 60 years of age.
4. When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s critical to know when to get medical assistance for signs of lower leg clot. Seeking medical advice from professional is advised if you encounter:
- One leg experiencing sudden swelling
- Severe pain that is not same as regular muscle cramp
- Warmth in leg
- Skin discoloration
In event that you encounter any pulmonary embolism symptoms including but not limited to:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Pain in chest particularly while inhaling deeply
- Blood in cough
Early treatment can greatly less chance of major consequences from lower leg clots.
5. Diagnostic Methods for Lower Leg Clots
Healthcare professionals can use number of techniques to identify lower leg clots including:
- Ultrasound: Non-invasive technique that visualizes venous blood flow and detects any clots using sound waves.
- D-dimer test: Blood test that detects presence of chemical released after blood clots break down. Elevated levels may be sign of clot development.
- CT or MRI scan: Imaging methods that provide finely detailed images of blood vessels, facilitating the detection and evaluation of clots and their severity.
6. Treatment Options for Lower Leg Clots
- Anticoagulants: Drugs that help prevent new clots from forming and enable body to break down existing clots. Warfarin and recent alternatives such as rivaroxaban and apixaban are common anticoagulants.
- Thrombolytics: Clot-busting drugs can be used to quickly dissolve large clots in extreme situations.
- Compression stockings: By preventing post-thrombotic syndrome and reducing edema, compression stockings can be used.
- Lifestyle changes: For both prevention and treatment it is important to include regular physical activity, maintain healthy weight and avoid long immobility.
7. Preventive Measures Against Lower Leg Clots
Number of preventive measures are needed to prevent lower leg cramps:
- To promote proper blood circulation participate in frequent physical activity.
- Maintaining ideal blood viscosity can be achieved by drinking plenty of water.
- Compression stockings can help improve circulation in people who are more sensitive.
- Take stops to stretch and walk while traveling long distances.
- Maintaining healthy weight can reduce venous pressure.
8. Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk of Lower Leg Clots
- Regular exercise: Try to do at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise week. Leg strengthening exercises can be specially helpful.
- Healthy diet: Vascular health can be supported by balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein.
- Avoid smoking: Quitting smoking helps increase blood circulation and reduces chances of blood clots.
- Frequent checkups: Seeing doctor on regular basis can help monitor risk factors specially for individuals who have underlying medical disorders.
9. FAQ’s
Q: Are clots in lower legs deadly?
A: Yes, It is possible for clot to become dislodged and move to lungs causing potentially fatal pulmonary embolism.
Q: Is it possible to prevent lower leg clots?
A: While not clots can be prevented, living healthy lifestyle and implementing preventive steps can considerably lower risk.
Q: How much time does recovery take following clot in lower leg?
A: Length of recovery can vary based on treatment strategy and severity of clot but many people can return to their regular activities in few weeks to months.
Q: Are lower leg clots more likely to occur during pregnancy?
A: Yes, hormonal changes and increased venous pressure during pregnancy increase risk of blood clots. Expectant women should be aware of signs of DVT and take precautions such as exercising and if advised wearing compression stockings.
10. Conclusion
It is important to understand symptoms of lower leg clots and to diagnose them early. By knowing indicators and risk factors, getting right medical help and implementing preventive measures, individuals can dramatically reduce their risk of developing clot in lower leg. You can take charge of your health and well being by being informed.
